The AI Open Source Landscape is not just a project directory, but an innovative attempt to bring transparency and quantifiability to the AI open source ecosystem.
Note: This article is intended for general readers and focuses on platform features and usage scenarios. If you want to see the technical details and formulas behind the scoring, please refer to: AI Project Scoring and Inclusion Criteria.
Project Background and Positioning
The AI Open Source Landscape aims to provide developers, researchers, and enterprise users with a one-stop navigation and evaluation platform for AI open source projects. With the rapid development of large language models (LLM, Large Language Model), multimodal models (Multimodal Model), and other AI technologies, the open source community has seen a surge of innovative projects. However, information is scattered and quality varies, making it difficult for users to filter and make decisions.
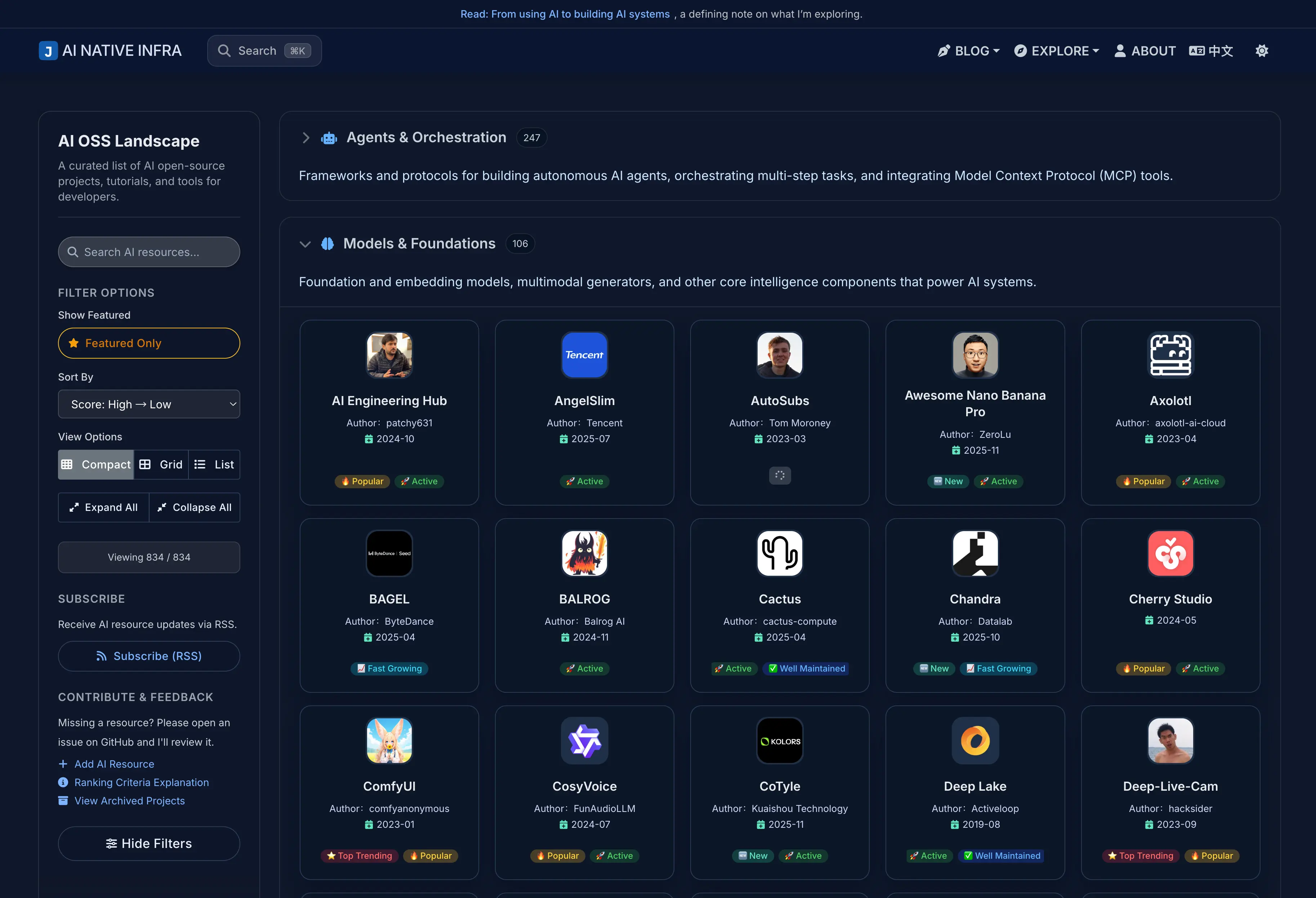
The AI Open Source Landscape systematically collects mainstream AI open source projects. As of the time of writing, it has included 851 open source projects. This landscape combines a multi-dimensional scoring system to help users efficiently discover, compare, and select the most suitable AI tools and frameworks for their needs. The platform not only focuses on models themselves, but also covers datasets, inference engines, evaluation tools, application frameworks, and the entire ecosystem chain, striving to promote transparency, quantifiability, and sustainable development in the AI open source ecosystem.
Main Interface and Feature Highlights
The platform homepage presents project distribution in both landscape and list views, supporting category filtering, keyword search, and tag navigation to help users quickly locate target projects.
For general readers, the main experience points include:
- Card view: One-sentence overview, star rating, and overall score for quick browsing and comparison.
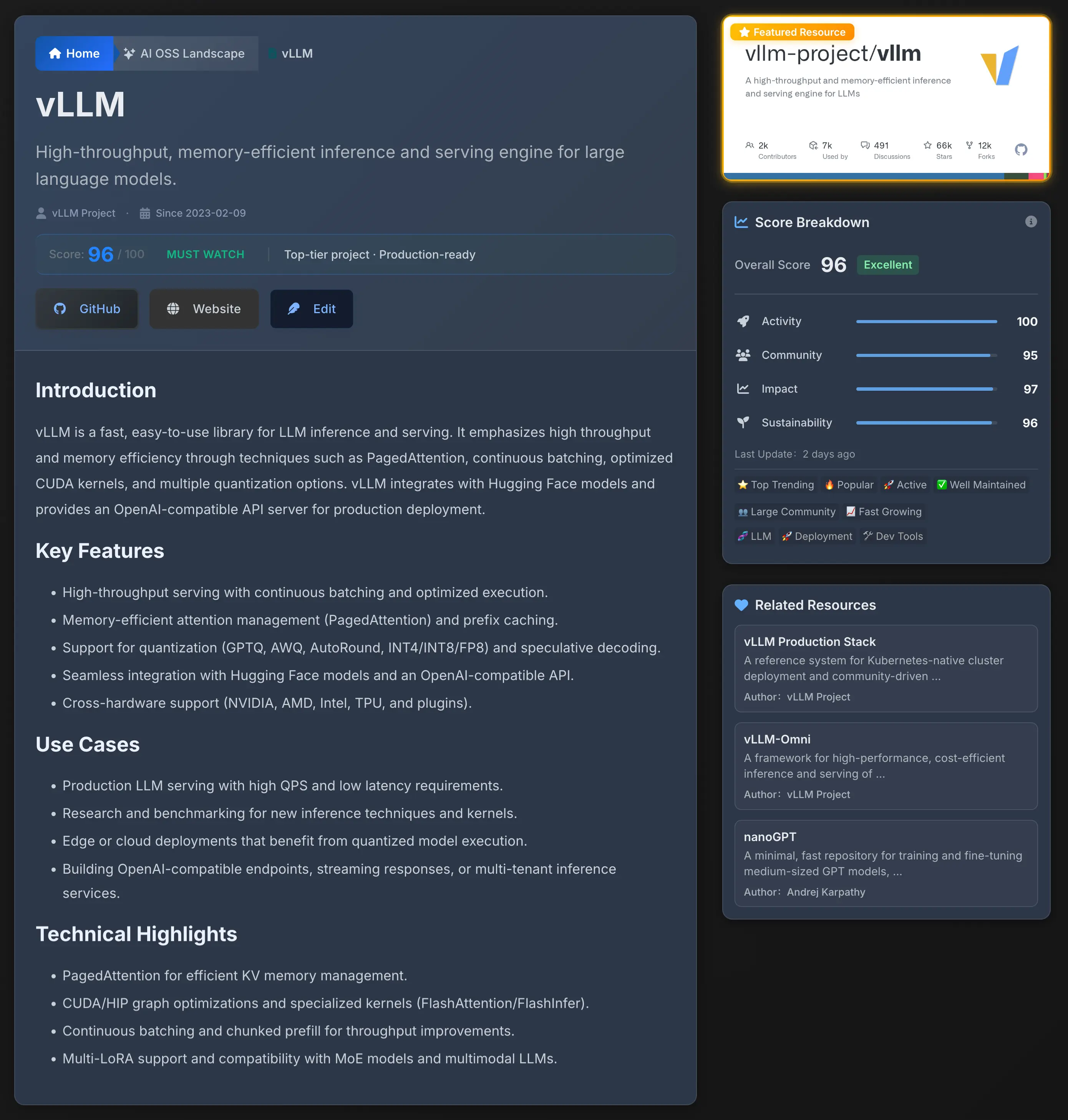
- Health card: Displays overall health and key dimensions (activity, community, influence, sustainability) on the project page or sidebar, with the latest update marked for easy assessment of maintenance status.
- Detail page: Provides more background information, project links, and application scenarios to help you evaluate suitability for your needs.
- Smart badges: Visually display labels such as “Active”, “New Project”, “Popular”, “Archived” on cards, helping you quickly capture key project features.
If you are interested in the specific rules for badge determination or scoring, detailed explanations are available on the Scoring Rules Page.
Scoring and Ranking Mechanism
The platform uses multi-dimensional scores to reflect the overall health and popularity of projects. The main dimensions include: Activity, Community, Quality, Sustainability, and the comprehensive Health score. These scores help you quickly judge whether a project is suitable for production or experimentation.
Data Sources and Update Mechanism
The platform’s data mainly comes from GitHub, project lists, official documentation, and community recommendations. We regularly and automatically synchronize and update metrics to ensure that the “last updated” and scores displayed on the interface reflect the current maintenance status of projects. Projects that have not been updated for a long time or are determined to be “inactive” are moved to the Archived Page. Archived projects remain searchable and retain historical scores, but will not appear in the default view of active rankings, making it easier for readers to focus on projects that are still maintained and active.
For general readers, the key points are:
- The page displays key metrics and “last updated” time, helping you quickly judge whether a project is still maintained.
- The AI Open Source Landscape continuously iterates on the scoring model to improve fairness and differentiation.
How to Contribute and Correct Data
If you want a project to be included or its data updated, you can:
- Submit an AI Open Source Project Inclusion Request
- Keep the project’s README, License, documentation, and other information complete in the repository to facilitate our data collection and assessment.
- For faster synchronization or if you encounter data issues, contact the maintainers via project issues or raise a request in the site discussion area.
Typical Use Cases or User Feedback
The AI Open Source Landscape has been widely used in various scenarios such as AI developer selection, enterprise technology research, and academic studies. For example:
- Developers can quickly filter models or tools that meet their needs through the platform, saving significant research time.
- Enterprise technical teams use the ranking lists for competitor analysis and technology planning.
- Educational and research institutions refer to the landscape to understand trends in the AI open source ecosystem, supporting course design and topic selection.
Some users have commented that the platform is “comprehensive, well-structured, and fair in scoring,” greatly improving the efficiency of AI project selection and learning. Community suggestions continue to drive ongoing improvements in platform features and content.
Summary
The AI Open Source Landscape systematically and quantitatively organizes the AI open source ecosystem: the backend worker is responsible for reliable data collection and scoring calculations (supporting backfill and migration), while frontend components handle fast rendering and visualization (including smart badges, health cards, and metric explanations).
If you want to learn more about the scoring details or participate in improvements:
The community is welcome to join in evaluation, backfilling historical data, and refining scoring rules, working together to make the AI open source ecosystem more transparent and sustainable.
