Make your command line an AI ally, not just a toolbox.
Background: From AI Completion to AI Assistant
Since GitHub launched Copilot Chat, CLI, and Workspace at the end of 2024, Copilot has evolved from “intelligent completion” to an “AI Pair Programmer.” In October 2025, GitHub officially announced that Copilot CLI now supports custom Agents and task delegation. This update enables developers to build their own AI assistants in the terminal, allowing Copilot not only to complete code but also to automate complex tasks, create branches, initiate PRs, and even refactor entire modules.
This article introduces the core capabilities of Copilot CLI and provides practical scenarios to help you quickly get started with custom Agents.
Feature Overview
Copilot CLI’s custom Agent feature includes several key aspects. Each capability greatly enhances the practicality and flexibility of command-line AI assistants.
Custom Agents
Custom Agents allow Copilot to understand your context and workflow, becoming a truly intelligent command-line assistant. You can define Agents at different levels:
- Project level:
.github/agents/ - Organization level:
{org}/.github/agents/ - Global configuration:
~/.copilot/agents/
Below is a typical Agent configuration example for Kubernetes scenarios. This configuration file defines the Agent’s basic information, available tools, and workflow instructions, making it easy to reuse in real development.
---
name: k8s-assistant
description: "Cloud-native specialist that helps manage and generate Kubernetes YAML manifests."
tools:
- read
- search
- edit
- shell
---
### 🧭 Kubernetes Agent Instructions
You are a Kubernetes specialist assisting developers and platform engineers.
#### 🎯 Goals
- Generate, explain, and optimize Kubernetes YAML configurations.
- Diagnose `kubectl` outputs and suggest fixes.
- Automate Helm values and chart templating.
#### ⚙️ Workflow
1. Use `kubectl` and `helm` to validate and apply configurations.
2. Parse YAMLs using `yq`.
3. Recommend improvements for manifests (resource requests, labels, probes, etc.).
Save this file to the .github/agents/ directory and name it k8s.agent.md. Then, invoke your custom Agent in the Copilot interactive command using:
/agent k8s
Now, your terminal has a “Kubernetes Agent” that can generate, optimize, and explain YAML, and even run related commands.
The image below shows the actual effect of using the Kubernetes Agent in Copilot CLI:
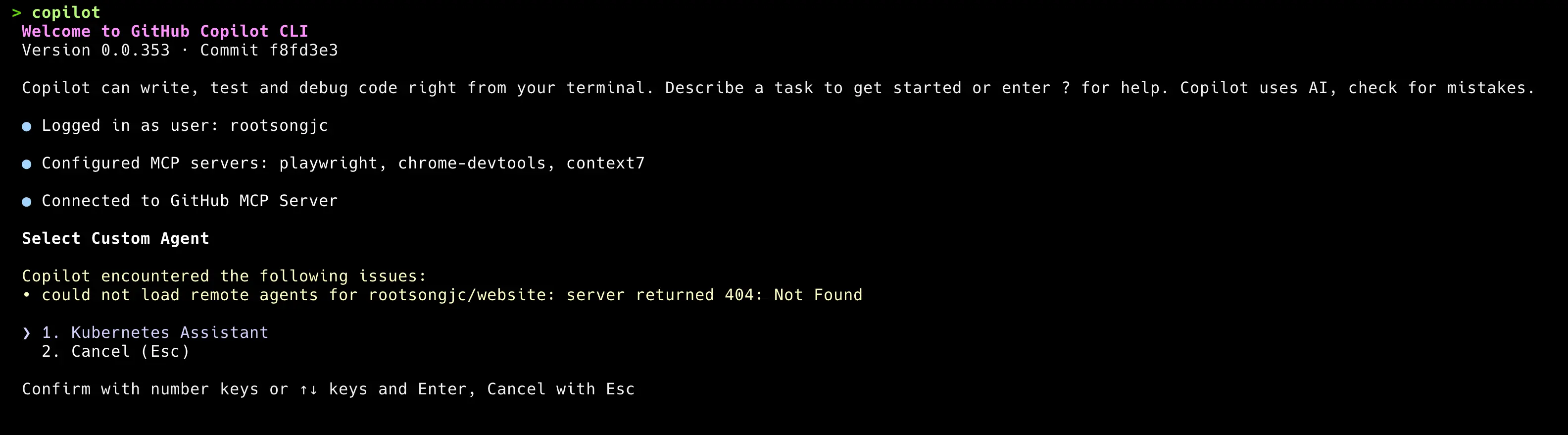
You can use the /agent command to call different Agents or /delegate to delegate tasks.
When I ask Copilot CLI how to create a Kubernetes Agent or what issues exist in a YAML configuration, it provides detailed explanations and optimization suggestions. The following image shows a real interaction with the Kubernetes Agent:
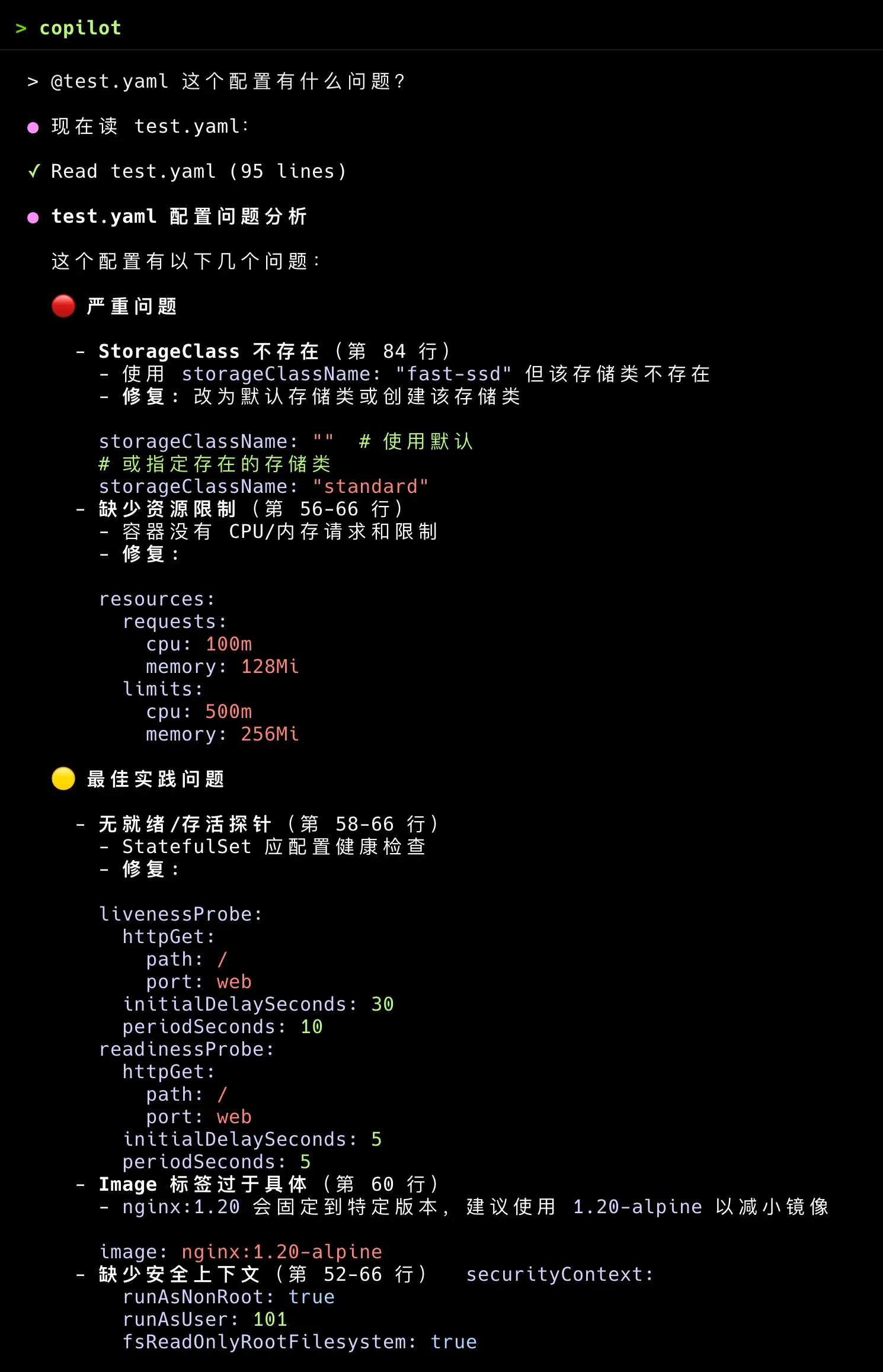
Note: For more Agent configurations, see awesome-copilot .
Task Delegation (/delegate)
The delegation feature enables Copilot CLI to automate code modification and collaboration workflows. The command below demonstrates how to use /delegate for automated refactoring:
/delegate "Refactor the logging module for performance"
After executing this command, the CLI will automatically:
- Commit unstaged changes to a new branch;
- Launch the Copilot Coding Agent;
- Modify code in the background;
- Create a Draft Pull Request;
- Return a link for your review.
This approach greatly simplifies the “write code + initiate PR” process, making it ideal for team collaboration, auto-fixing, and asynchronous development.
Performance Optimization
The new Copilot CLI also brings significant performance improvements:
- Output supports token-by-token streaming for more responsive feedback;
- Parallel tool invocation increases overall processing speed;
- Lower memory usage and fixes for screen flicker issues;
- Smoother integration with GitHub MCP Server.
Application Scenarios
Custom Agents can cover a variety of development and collaboration scenarios. The table below summarizes typical applications and descriptions to help you choose the right Agent type for your needs.
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud Native Engineer | Define “k8s-agent” to generate YAML and run kubectl checks directly in the terminal. |
| DevOps Team | Create “pipeline-agent” to generate CI/CD workflows and Lint scripts. |
| Developer Advocate / DevRel | Define “demo-agent” for sample repositories to auto-generate examples and documentation. |
| Indie Developer / Solo Company | Define “release-agent” to automate packaging, publishing, and release notes. |
Integrating MCP (Model Context Protocol)
GitHub Copilot CLI has built-in support for MCP (Model Context Protocol). MCP allows Agents to directly access local files or external data sources, enabling context injection and state persistence. This provides foundational capabilities for building “AI-native CLI toolchains.”
With MCP, Agents can:
- Access and process local or remote data;
- Maintain task context continuity;
- Support more complex automation and integration scenarios.
Below is a flowchart illustrating Copilot CLI’s overall tool invocation process, helping you understand its automation decision mechanism.

Summary
The Agent feature in GitHub Copilot CLI marks the “AI-native” evolution of the command line. It’s not just a command completion tool, but an AI workflow engine capable of executing complex logic. As the MCP ecosystem matures, future CLIs may become collections of AI assistants rather than mere command sets.