Istio is a powerful service mesh solution that provides zero-trust security, observability, and advanced traffic management without requiring code modifications. However, misconfigurations often lead to unexpected behavior. This article discusses several common Istio configuration errors, explains the principles behind them, and shows how to identify and resolve these issues through diagrams. We will also introduce the TIS Config Analyzer tool from Tetrate, designed to optimize Istio operation efficiency and security.
Incident Cases Caused by Configuration Errors
Here are two typical incidents caused by configuration errors:
Amazon Web Services 2017 Outage: A simple typo led to widespread service disruptions, affecting thousands of online services and applications, highlighting that even a minor configuration error in mature cloud infrastructure can have severe consequences.
GitLab 2017 Data Loss Incident: Due to configuration errors, GitLab accidentally deleted a large amount of production data during database maintenance. Although backup mechanisms were configured, an incorrect configuration prevented timely data recovery.
These cases show the importance of proper configuration management in preventing service disruptions and data loss.
Common Types of Istio Configuration Errors
Istio configuration errors can be broadly categorized as follows:
- AuthorizationPolicy: Non-existent namespaces, HTTP methods and fully qualified gRPC names only, host without matching service registry entries, fields requiring mTLS enabled, missing service accounts, etc.
- DestinationRule: Multiple destination rules for the same host subset combination, host without matching entries in the service registry, subset labels not found in any matching hosts, etc.
- Gateway: Multiple gateways for the same host-port combination, gateway selectors not finding matching workloads in the namespace, etc.
- Port: Port names must follow a specific format, application protocols for ports must follow a specific format, etc.
- Service: No deployments exposing the same ports as the service found, etc.
- VirtualService: Routes with target weights do not have a valid service, virtual services pointing to non-existent gateways, etc.
Common Istio Configuration Errors Examples
In daily use of Istio, here are some of the most common configuration errors:
Virtual services pointing to non-existent gateways:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: details namespace: bookinfo spec: hosts: - details gateways: - non-existent-gatewayIn this case, the
detailsvirtual service tries to route through a non-existentnon-existent-gateway, leading to traffic management failure.Virtual services referencing non-existent service subsets:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: details namespace: bookinfo spec: hosts: - detailsIf the
detailsservice does not define the corresponding subsets, requests will be rejected due to not finding the correct service instances.Gateways not finding specified server credentials:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1 kind: Gateway metadata: name: cert-not-found-gateway namespace: bookinfo spec: selector: istio: ingressgateway servers: - port: number: 443 name: https protocol: HTTPS tls: mode: SIMPLE credentialName: "not-exist"This will lead to a TLS handshake failure because the specified credential
not-existdoes not exist.
Configuration Verification
To reduce the risk of service disruptions due to configuration errors, configuration verification has become indispensable. Configuration verification can be divided into the following two types:
- Static Configuration Verification: Verify configurations before they are applied to the system. This includes checking for syntax errors, completeness, and validity of configuration items.
- On-demand Configuration Verification: Verify configurations that have already been applied but may need adjustments based on real-time data. This type of verification helps adapt to changes in dynamic environments, ensuring the ongoing correctness of configurations.
Recommended Configuration Verification Tools
istioctl validate
istioctl validate is used to verify the syntax and basic structure of Istio configuration files (such as YAML files), ensuring that the configuration files comply with the Istio API specifications. It can detect syntax and format errors before configurations are applied to the cluster. This is a static analysis tool, often integrated into the CI process, to prevent invalid configuration files from being applied to the cluster.
istioctl analyze
istioctl analyze is a powerful diagnostic tool used to analyze the operational state and consistency of configurations in an Istio cluster. It not only checks the syntax of configuration files but also examines the configurations applied in the cluster to identify potential problems and conflicts. istioctl analyze provides dynamic analysis capabilities, capable of identifying configuration errors and potential issues during cluster operation.
The configuration process for istioctl analyze is as follows:
- Collect Configuration Data: First,
istioctl analyzecollects Istio configuration data from specified sources. These sources can be an active Kubernetes cluster or local configuration files. - Parse and Build Model: The tool parses the collected configuration data and builds an internal model representing Istio configurations.
- Apply Analysis Rules: Subsequently, it applies a set of predefined rules to analyze this model, detecting potential configuration issues. These rules cover a range of potential issues from security vulnerabilities to performance problems.
- Generate Report: After the analysis is complete,
istioctl analyzeoutputs a detailed report containing all identified issues. If no issues are found, it informs the user that the configurations appear to be correct.
The following is a workflow diagram of istioctl analyze:
Kiali
Kiali is a crucial tool for managing and visualizing Istio service meshes, providing real-time insights into the mesh’s health, performance, and configuration status. By integrating Kiali into your Istio environment, you can enhance configuration security through:
- Visualization: Kiali offers a graphical representation of the service mesh, making it easier to spot configuration errors, such as incorrect routing or missing policies.
- Validation: It helps validate Istio configurations, highlighting issues such as misconfigured gateways or destination rules before they cause problems.
- Security Insights: Kiali provides visibility into security policies, ensuring that mTLS and authorization settings are correctly implemented.
Using Kiali alongside tools like istioctl validate and istioctl analyze ensures a more robust approach to preventing and resolving Istio configuration errors, contributing to a secure and efficient service mesh.
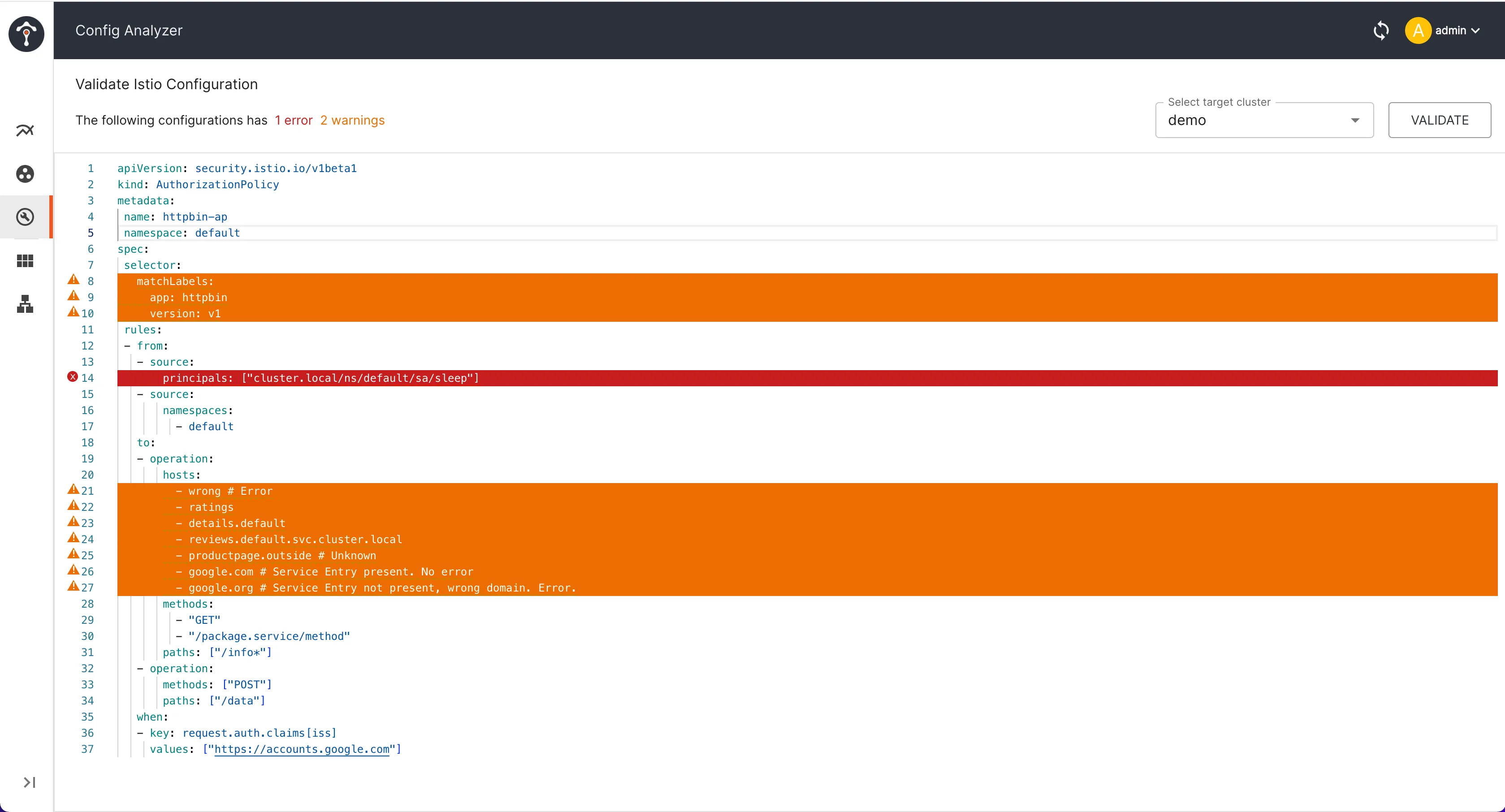
Introduction to TIS’s Config Analyzer Tool
To help developers and operations staff avoid common configuration mistakes, Tetrate developed the Config Analyzer tool in the TIS Dashboard. This tool automatically verifies Istio configurations, analyzes service mesh configuration issues based on best practices, and provides optimization suggestions. Config Analyzer can automatically detect configuration issues in the Istio service mesh, offering explanations and solutions, and supports on-demand error detection in configurations.
Conclusion
Properly configuring Istio is key to ensuring the healthy operation of the service mesh. By understanding and avoiding common configuration errors, and using advanced tools like Tetrate’s TIS Config Analyzer, you can ensure the stability and security of your Istio environment. Remember, a small configuration error can lead to a failure of the entire service mesh, making continuous monitoring and auditing of configurations very necessary.
References
This blog was initially published at tetrate.io.