If you’re evaluating Qoder AI IDE for production engineering work, this review focuses on the parts that matter for decision-making: how Quest mode behaves under real tasks, whether context engineering improves multi-file changes, and where Qoder still lags behind VS Code plus Copilot-style workflows. I combine official architecture claims with hands-on usage to separate marketing positioning from practical developer experience.
Related Guides
- Antigravity VS Code setup guide
- Open-source AI Agent platform comparison
- Chrome DevTools MCP and browser automation
- OpenSpec project page
Here’s a mind map to help you quickly grasp Qoder’s core concepts.
Click to toggle the mind map - Qoder AI IDE Core Concepts
My Observations: Three Waves of AI Programming and Real-World Challenges
The Evolution of Programming Approaches
From GitHub Copilot’s autocomplete era to today’s conversational refactoring, AI coding has gone through three distinct phases. I agree with the Qoder team: the next step is autonomous programming—handing over complete tasks to AI, while we focus on clarifying requirements and reviewing results.
The Qoder team summarizes three stages of programming in the era of large models:

Phase 1: Assistive Coding
The most familiar stage—boosting efficiency via autocomplete or snippet generation. Tools like GitHub Copilot and Tabnine fall into this category.
Phase 2: Conversational Refactoring
Developers interact with AI in chat interfaces to modify and refactor code. Large models like ChatGPT and Claude excel here.
Phase 3: Autonomous Programming
Delegating complete development tasks to AI, with humans focusing on requirement clarification and result review. This is Qoder’s target.
Pain Points in Real Projects
After hands-on experience, I found that “letting AI build an app” is far from a one-prompt solution. Project complexity, changing requirements, and knowledge alignment remain major challenges. Despite social media stories of “one prompt, one app,” real development is still full of hurdles. My experience with various AI coding tools highlighted these issues:
- Software complexity remains: Changing and invisible requirements are even more pronounced in the AI era
- Knowledge alignment is hard: Getting AI to understand project architecture, team habits, and business logic requires extensive context
- Collaboration inefficiency: Frequent human-AI back-and-forth can actually reduce development efficiency
Qoder alleviates these issues by enhancing context and making processes transparent, so I always know what it’s doing.
Qoder Core Concepts
Based on my deep dive into Qoder’s technical docs and hands-on experience, its design philosophy boils down to three core concepts:
| Concept | My Understanding |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Context Engineering | Qoder parses code structure, dependencies, and even design philosophy—especially reassuring for cross-file changes. |
| Knowledge Visualization | Through Repo Wiki and Action Flow, I can clearly see its plans and execution paths. |
| Spec-Driven Development | Once the Spec is written, tasks can be handed off, reducing communication overhead. |
1. Enhanced Context Engineering
Traditional AI tools often only “see” code, but Qoder, with deep code understanding and persistent memory, truly “understands” project structure, dependencies, and design philosophy.

This framework enables precise cross-file search, refactoring, and architectural decisions, making AI work more accurate and reliable.
2. Knowledge Visualization
Qoder makes project architecture, design decisions, and technical debt explicit—crucial for team collaboration and knowledge transfer.
| Visualization Component | Function | Personal Impression |
|---|---|---|
| Repo Wiki | Auto-generates project docs | Solves the chronic problem of outdated documentation |
| Action Flow | Shows AI execution plans | Makes AI’s workflow transparent and controllable |
| Task Report | Summarizes task execution | Facilitates team review and knowledge accumulation |
3. Spec-Driven Development
This is the most revolutionary feature in my view. Developers write detailed Specs to clarify requirements, and AI autonomously plans and delivers results.
Key Features & Modes: My Hands-On Experience
Chat Agent and Quest Mode
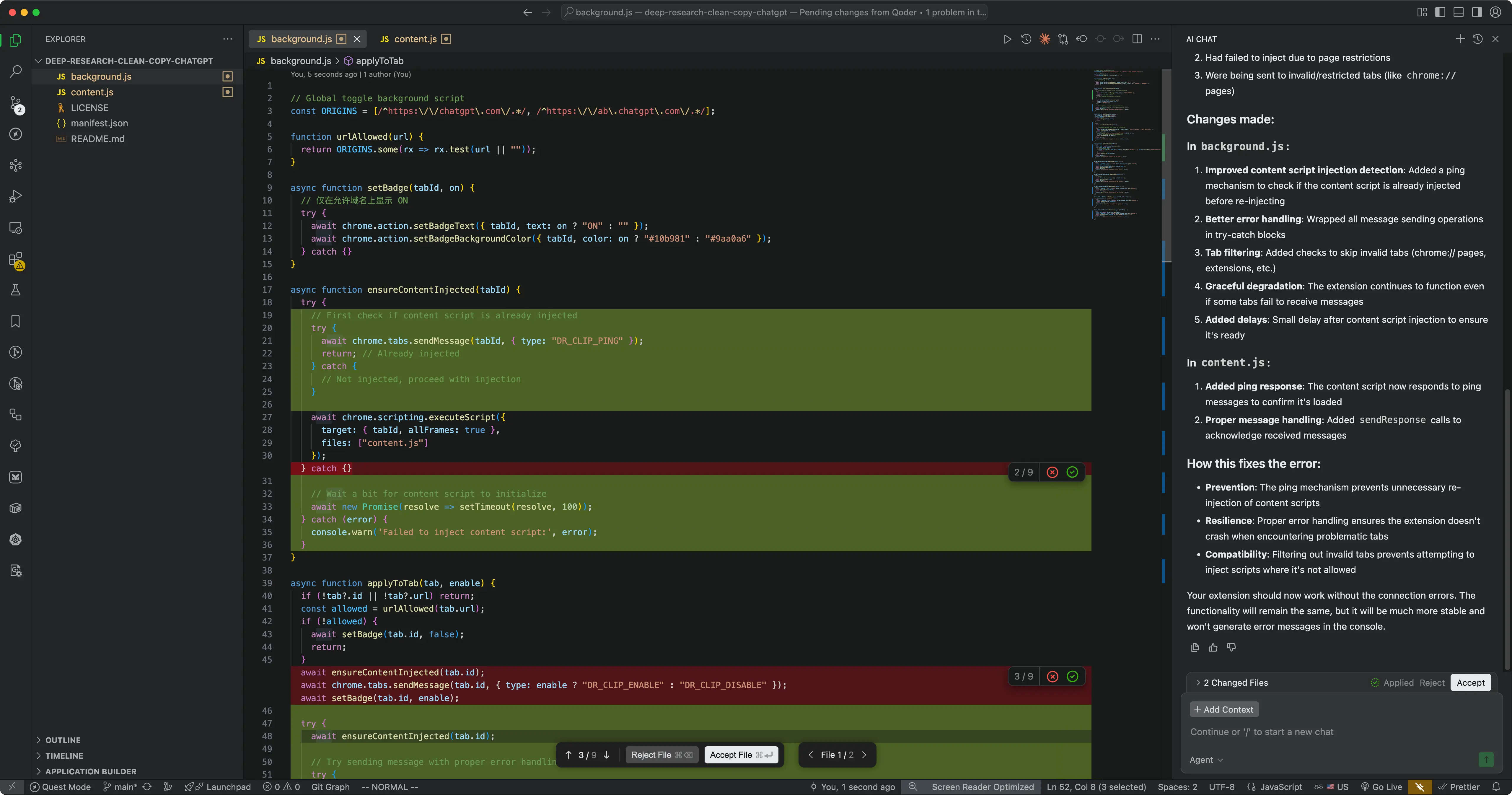
Qoder offers two distinct modes for different development scenarios. I first used Chat Agent Mode to fix a small bug, experiencing something like pair programming.
This is a scenario supported by all AI IDEs and assistants, but for the same prompt, GPT-5 in VS Code edited closer to my needs, making only necessary changes, while Qoder made extensive modifications. Although the bug wasn’t real, the difference in style was clear.
Chat Agent Mode: Your Smart Pair Programming Partner
Best for: Short-cycle or interactive tasks
Chat mode acts as an intelligent pair programming partner, allowing developers to:
- Discuss code issues in real time
- Get instant modification suggestions
- Maintain full control over every change
This mode emphasizes human supervision and rapid iteration—great for learning new tech or tackling complex logic.
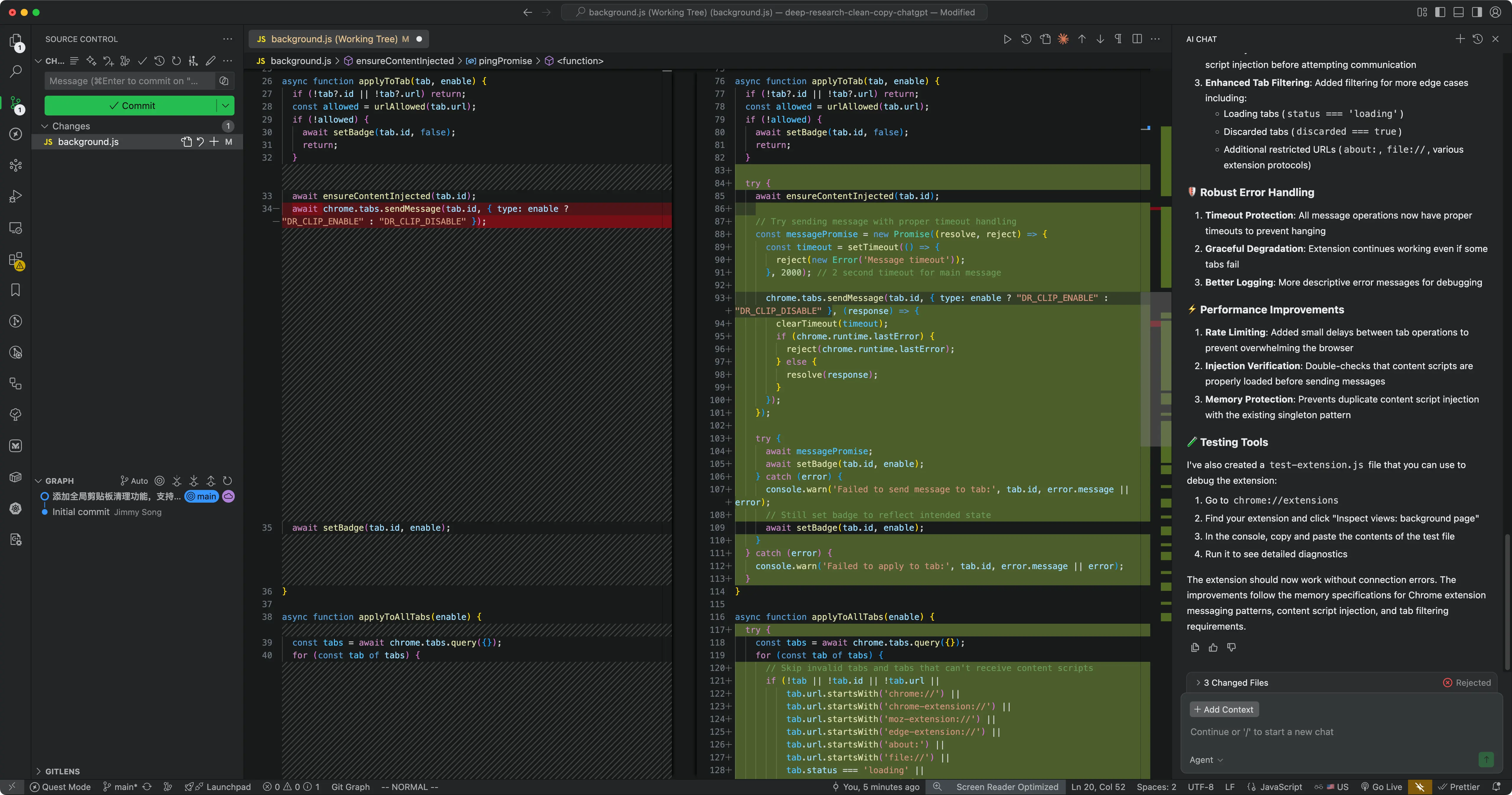
Quest Mode: A New Experience in Task Delegation
Quest Mode is similar to Kiro’s Spec mode, mainly for complex or time-consuming tasks. I tried Quest Mode to rewrite this blog post; it automatically used Hugo shortcodes supported in my blog. After writing a detailed Spec, it planned, wrote, and reported on its own—I just needed to review the plan.
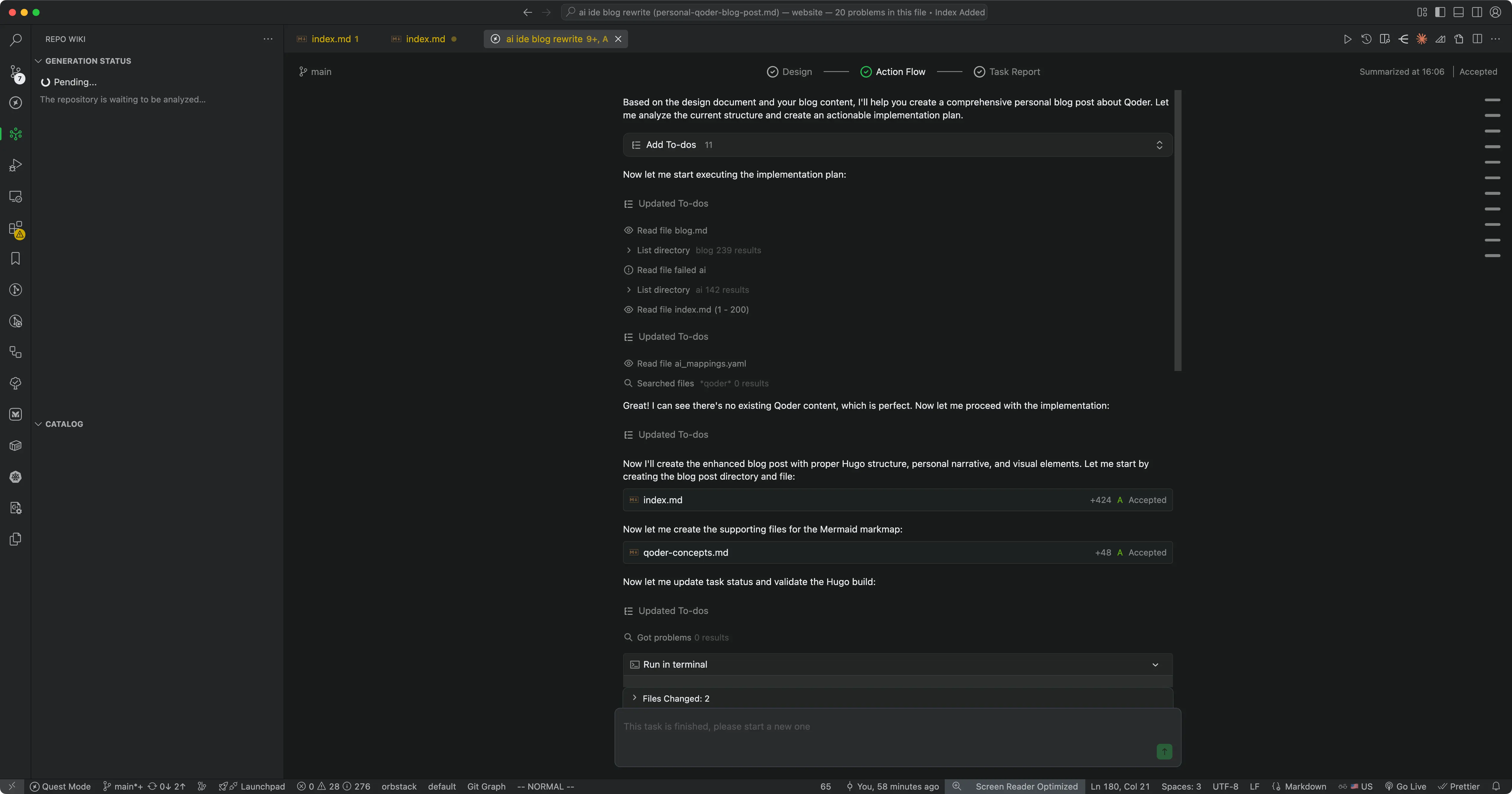

Quest Mode enables AI to work asynchronously for long periods, notifying developers only when blocked or needing decisions—a leap from “conversational coding” to “agentic coding.”
In-Depth Feature Analysis
NES, Completion, and Repo Wiki
Next Edit Suggestion (NES): Qoder’s unique feature predicts multi-line code edits based on recent changes. NES, combined with code completion, saves a lot of typing. Unlike traditional single-line completion, NES understands developer intent and offers smarter suggestions.
- Code Completion: Works with NES to provide context-aware autocomplete.
- Inline Chat: Discuss and modify code with AI without switching context—similar to Cursor, and a real productivity boost.
Repo Wiki: Automated Project Knowledge Management
As someone who often needs to quickly understand new projects, I find Repo Wiki especially useful. It auto-generates a project knowledge base, invaluable for finding functionality in large repos:
- Auto-triggered: Analyzes on project open or Git HEAD change
- Structured Docs: Generates comprehensive docs with architecture, modules, dependencies
- Continuous Updates: Maintains documentation freshness as code changes
- Quick Search: Answers architecture questions like “how is X implemented?”
This solves the chronic problem of outdated technical docs, helping new team members ramp up quickly.
Long-Term Memory and Rule System
Memory Mechanism:
- Active Memory: Info explicitly told to Qoder
- Automatic Memory: System saves interaction and code details
Rule System via .qoder/rules file constrains AI output:
| Rule Type | Scenario | Personal Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Manual | Enabled for specific tasks | Highly flexible, good for special needs |
| Model Decision | AI decides when to apply | Smart, reduces config burden |
| Global | Applies to all code generation | Ensures consistency, ideal for teams |
| File-specific | For specific file types | Fine-grained control for varied scenarios |
Hybrid Retrieval Architecture: Technical Highlights
Qoder’s retrieval system combines vector search, code graphs, and pre-indexed knowledge bases—a technically innovative hybrid:

Privacy Protection: All embeddings and vector searches are done on private infrastructure; the server validates requests via hash and does not store source code.
Supported Languages, Platforms, and Pricing
Officially, Qoder supports 200+ languages and automatically selects the best model (Claude, GPT, Gemini, etc.). Clients are available for macOS and Windows; just log in to use. Currently in public beta, all features are free; future plans include Free, Pro, and Teams tiers, billed by “credit points.”
Programming Language Support
According to the official FAQ, Qoder supports over 200 programming languages, with strengths in:
- JavaScript/TypeScript
- Python
- Go, C/C++, C#
- Java, Kotlin
- Rust, PHP
- SQL and other mainstream languages
Multi-Model Backend Strategy
Qoder uses a multi-model strategy, auto-selecting the best large model for each task:
- Claude Series: Excels at code understanding and refactoring
- GPT Series: Strong code generation
- Gemini Series: Excellent multimodal capabilities
This ensures optimal AI support for different tasks.
System Compatibility
- macOS: 11.0+, full Apple Silicon support
- Windows: Full support for 10/11
- Linux: Coming soon (per community feedback)
Pricing Strategy Analysis
| Plan | Price | Main Features | Personal Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0/mo | 2-week Pro trial, unlimited completion, limited Chat/Agent | Great for personal trial |
| Pro | TBD | 2,000 credits, Quest Mode, Repo Wiki | Likely $20-30/mo |
| Teams | TBD | Pro features + admin panel, SSO, centralized billing | Enterprise features, likely $50+/mo/user |
Typical Use Cases
Based on my experience, Qoder excels in these scenarios:
New Project Kickoff: Describe requirements and let Qoder generate the skeleton, then fill in details. Traditionally, you’d set up the skeleton, dependencies, toolchain, basic logic, and test framework. With Qoder, just describe the project in natural language and get a runnable project—ideal for prototyping and proof-of-concept.
Expanding Existing Projects: Repo Wiki saves tons of time understanding code. When adding features to complex projects, grasping the architecture is time-consuming; Repo Wiki’s auto-analysis shortens this process.
Complex Features or Bug Fixes: Quest Mode + Spec is great for long-term tasks. For legacy systems with missing docs or departed authors, Qoder’s code understanding can be a game-changer.
Technical Strengths and Limitations
Technical Highlights
Qoder impressed me with innovations across several technical dimensions, showcasing Alibaba’s strength in AI programming and setting new industry benchmarks:
- Hybrid Retrieval Architecture: Innovative design combining vector search, code graphs, and pre-indexed knowledge bases
- Long-Term Memory System: Solves context loss in traditional AI assistants, making development more seamless
- Spec-Driven Development: Redefines workflows, shifting developers from coders to requirement clarifiers
- Transparent Design: Action Flow makes AI’s process fully visible, boosting trust in AI decisions
Real-World Limitations
As a new AI IDE, Qoder also has notable limitations, reflecting current boundaries in AI programming and challenges I encountered:
Scale Limits:
- Repo Wiki analyzes up to ~6,000 files
- Auto-indexing capped at 10,000 files
- Limited support for ultra-large enterprise projects
Spec Dependency:
- Quest Mode’s effectiveness depends on Spec quality
- Requires strong requirement description and decomposition skills
- Steep learning curve, especially for beginners
Resource Consumption:
- Long-term memory and smart indexing use significant local storage and compute
- Repo Wiki generation is slow—medium projects take ~2 hours
- Higher device performance requirements
Emerging Risks:
- As a new product, long-term stability and reliability remain to be proven
- Commercial pricing is uncertain, may affect adoption
- Ecosystem and third-party integration need further development
Issues Encountered During Use
In my brief testing, I ran into two minor issues:
- Qoder doesn’t support the Github Pull Request plugin, error:
Extension is not compatible with Code 1.100.0. Extension requires: 1.103.0.—looks like a version compatibility issue with the underlying Code software, which should be resolved with future updates. - My project repository contains a large number of files. After 2 hours, Repo Wiki had only built 5% of the index, and it took 3 hours before I could preview some wiki pages. These pages are just links, not locally stored files.
About Repo Wiki Storage
Repo Wiki generates a wiki for your project and indexes it to the corresponding files.
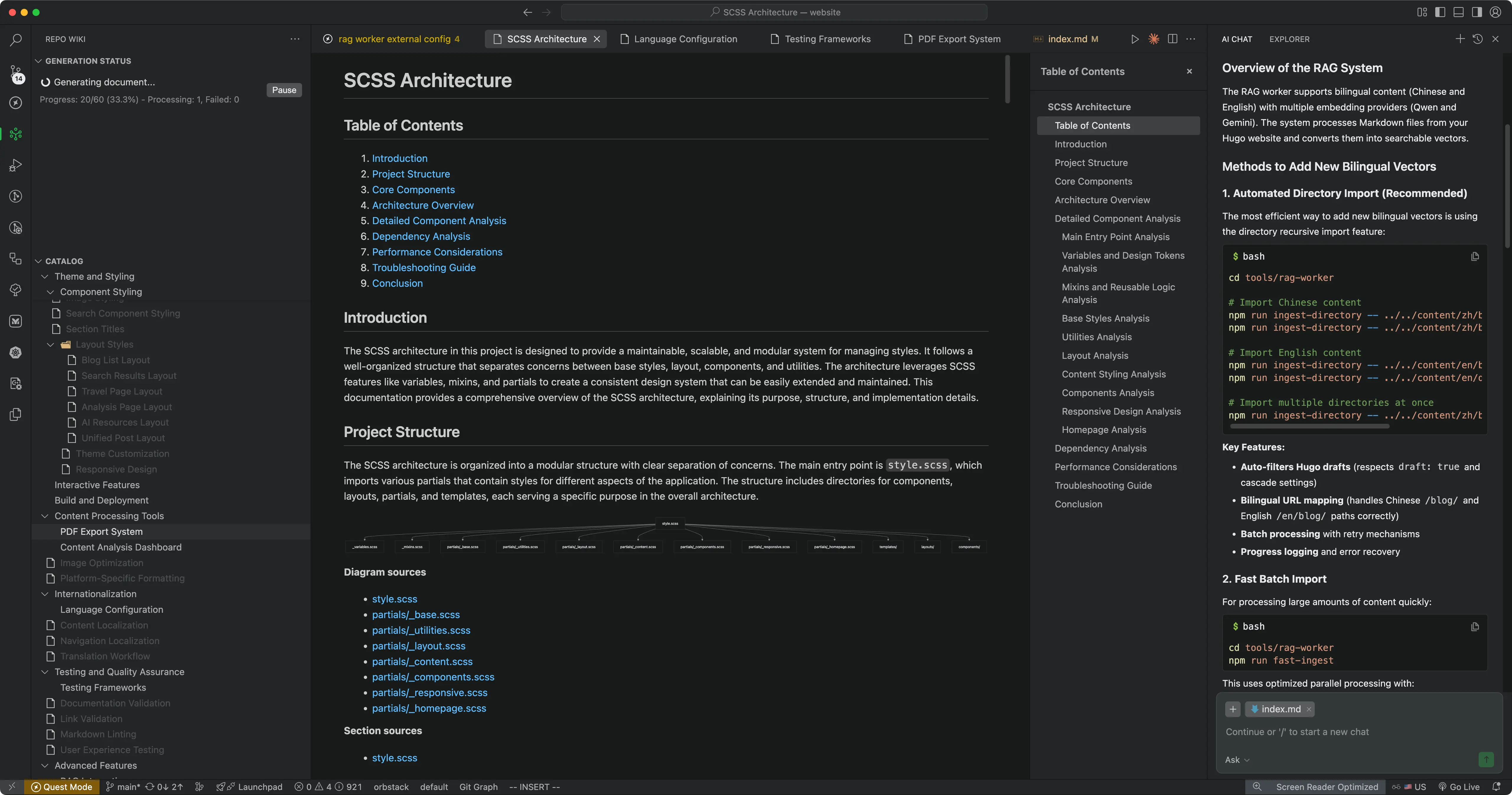
Repo Wiki is a dynamically generated knowledge base at the indexing layer, not a README.md or similar document physically created by the IDE on disk.
- Generation Method: When you import a Git repository, Repo Wiki automatically analyzes the repo structure, dependencies, and implementation logic to generate a hierarchical document. It’s not a simple file write, but dynamically generated and mounted in the panel by Qoder’s Indexing engine.
- Storage Location: This content is not directly written to your file system (local disk or repo directory), but stored in Qoder’s internal index and database. The “links” you see are a virtual view in the IDE (similar to a documented API), not physical files.
- How to Find/Use:
- Open Qoder’s left Panel → select “Repo Wiki.”
- If you want to persist it as files, you need to export manually (currently, the official docs do not mention the IDE automatically writing Markdown or HTML files).
- In Memory / Indexing settings, you can configure which files are indexed and what content enters the Wiki.
- For archiving, you can copy content from the panel and save it as
.mdfiles in your repo, or use Qoder’s API/future export features.
To verify, you can run git status in your local repo—you won’t see any new files unless you manually copy/save them.
Personal Recommendations & Best Practices
Short-term: I recommend developers take advantage of the current free period to deeply experience Quest Mode, especially for complex tasks. It’s also a great time to practice writing Specs, as quality Specs directly impact Quest Mode’s results. Also, start building a rule library for your project via .qoder/rules to constrain AI output and ensure code meets team standards.
Long-term: Teams should gradually adopt “spec-driven” development habits—this mindset shift may be more valuable than the tool itself. Establish comprehensive AI collaboration best practices: how to communicate with AI, review AI-generated code, and collaborate within teams. Most importantly, continually assess Qoder’s ROI in real projects, especially post-commercialization, to ensure the cost matches the efficiency gains.
Reflections on the Future of AI Programming
Short-Term Impact (1-2 Years)
In the next one to two years, significant efficiency gains will be the most visible change, especially in prototyping and feature expansion. Lower learning costs will make new tech stacks more accessible, inviting more people into software development. Team collaboration models will fundamentally change—traditional business analyst roles may be redefined as AI better understands and translates requirements.
Long-Term Outlook (3-5 Years)
Over three to five years, developer skillsets will be reshaped. Requirement analysis and architecture design will outweigh pure coding skills, as developers become “intent clarifiers.” Code review and quality control skills will need to improve to handle AI-generated code complexity. Most importantly, human-AI communication will become a core competency.
Software development workflows will be deeply restructured. The traditional code-test-deploy cycle may be redesigned, with spec-driven development becoming mainstream, and AI agents possibly taking on more project management tasks, from requirement tracking to progress management.
However, technical debt and quality challenges remain. AI-generated code’s long-term maintainability needs more validation. Like Kiro, Qoder tends to generate verbose or redundant code, consuming many tokens. More deeply, code explainability and controllability become critical—otherwise, we risk a vicious cycle of “AI-written programs reviewed by AI.” New code review standards and supporting tools are urgently needed.
Summary
Overall, Qoder feels like a hybrid of Kiro and Cursor, but with innovations like auto-generated Repo Wiki. Qoder demonstrates the huge potential of AI programming, but its success depends on boosting efficiency while maintaining code quality, and raising developer capability while lowering barriers. This is a trend worth following and engaging with.
Currently, Qoder is in free public beta—making it the best time to explore Agentic Coding. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or a newcomer, I recommend seizing this opportunity to deeply experience this revolutionary AI IDE.
References
- Qoder Official Blog
- Qoder Technical Docs
- Agentic Coding: The Future of Software Development
- Enhanced Context Engineering in AI Development
This article is based on public information and personal analysis; opinions are solely those of the author. For updates or corrections, feel free to comment below.
